2025 Updated Food Guidelines for Ulcerative Colitis
The Importance of Diet in Managing Ulcerative Colitis
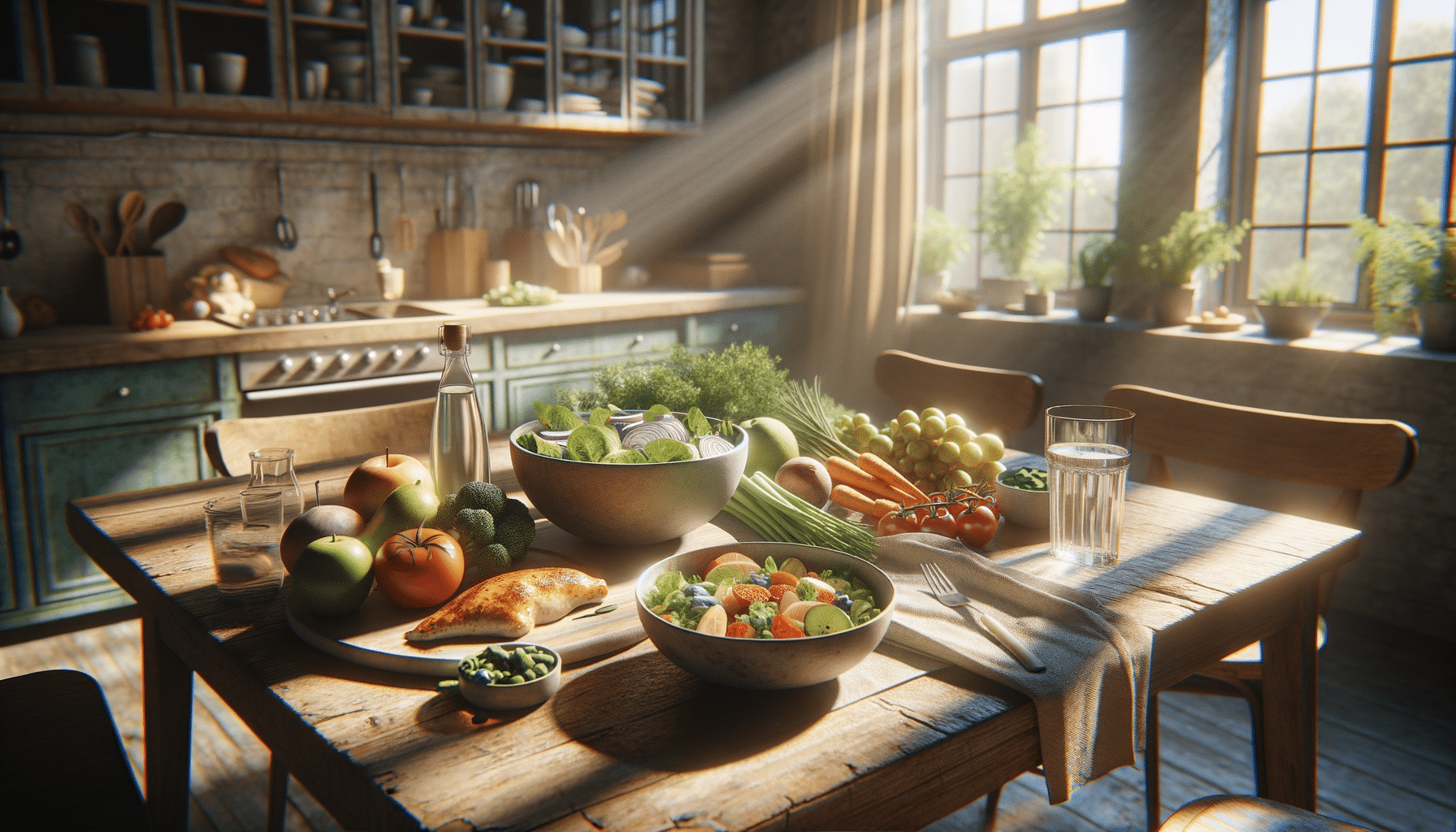
Understanding the impact of diet on ulcerative colitis is crucial for those seeking to manage this chronic condition. Ulcerative colitis, an inflammatory bowel disease, affects the lining of the colon and rectum, leading to symptoms such as abdominal pain, diarrhea, and fatigue. The 2025 Updated Food Guidelines for Ulcerative Colitis highlight the significance of dietary choices in mitigating these symptoms and promoting overall gut health.
While there is no one-size-fits-all diet for ulcerative colitis, certain dietary patterns can help reduce inflammation and improve quality of life. Key recommendations include consuming a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins while minimizing intake of processed foods and red meat. By focusing on whole, nutrient-dense foods, individuals can support their immune system and potentially reduce the frequency and severity of flare-ups.
Moreover, the guidelines emphasize the importance of personalized dietary plans. Since triggers can vary from person to person, working with a healthcare professional to identify specific food sensitivities is essential. This tailored approach ensures that individuals receive the nutrients they need without exacerbating their symptoms.
Key Components of the 2025 Dietary Guidelines
The 2025 Updated Food Guidelines for Ulcerative Colitis provide a comprehensive framework for dietary management. These guidelines are designed to offer flexibility while ensuring that individuals receive adequate nutrition.
Some of the key components include:
- Increased Fiber Intake: While high-fiber foods can be problematic during flare-ups, they are essential for maintaining gut health during remission. Patients are encouraged to gradually incorporate soluble fiber sources such as oats and bananas.
- Lean Proteins: Incorporating lean proteins like poultry and fish can help maintain muscle mass and provide essential amino acids without adding unnecessary fat.
- Hydration: Staying well-hydrated is crucial, especially during periods of diarrhea. Water, herbal teas, and electrolyte solutions are recommended.
- Probiotics: Fermented foods like yogurt and kefir can introduce beneficial bacteria into the gut, potentially aiding digestion and reducing inflammation.
These components work together to create a balanced diet that supports digestive health and minimizes the risk of exacerbating symptoms.
Foods to Avoid for Ulcerative Colitis Management
While the 2025 Updated Food Guidelines for Ulcerative Colitis encourage a diverse and balanced diet, they also identify specific foods that may trigger symptoms. Avoiding these foods can help manage the condition more effectively.
Some foods to be cautious of include:
- Spicy Foods: Foods with a high spice content can irritate the digestive tract and should be limited or avoided during flare-ups.
- High-Fat Foods: Fried foods and fatty cuts of meat can be difficult to digest and may increase inflammation.
- Dairy Products: For those who are lactose intolerant, dairy can exacerbate symptoms. Opting for lactose-free alternatives can be beneficial.
- Alcohol and Caffeine: These can irritate the bowel and should be consumed in moderation or avoided altogether.
By identifying and avoiding these potential triggers, individuals can better manage their symptoms and improve their overall quality of life.
The Role of Meal Planning and Regular Eating Habits
Establishing regular eating habits and planning meals can significantly benefit those with ulcerative colitis. The 2025 Updated Food Guidelines for Ulcerative Colitis stress the importance of consistency in meal timing and portion sizes to help stabilize digestion.
Here are some strategies to consider:
- Small, Frequent Meals: Eating smaller, more frequent meals can ease the digestive process and prevent overwhelming the gut.
- Mindful Eating: Paying attention to hunger cues and eating slowly can improve digestion and prevent overeating.
- Meal Prep: Preparing meals in advance ensures that nutritious options are readily available, reducing the temptation to reach for less healthy choices.
Implementing these practices can help maintain a balanced diet and reduce the incidence of flare-ups.
Personalizing Your Diet: A Collaborative Approach
The 2025 Updated Food Guidelines for Ulcerative Colitis emphasize the importance of a personalized approach to dietary management. Since individual responses to foods can vary, collaboration with healthcare providers is essential for developing a tailored dietary plan.
Key steps in personalizing your diet include:
- Keeping a Food Diary: Tracking food intake and symptoms can help identify specific triggers and patterns.
- Consulting a Dietitian: Working with a registered dietitian can provide expert guidance in creating a balanced and individualized diet plan.
- Regular Monitoring: Regular check-ins with healthcare providers can ensure that dietary adjustments are made as needed to accommodate changes in symptoms or nutritional needs.
This collaborative approach empowers individuals to take control of their health and manage ulcerative colitis more effectively.